In today’s time, getting clean and safe water is not as easy as it used to be. Due to pollution, chemicals, and industrial waste, various harmful elements get mixed in the water. In such a situation, Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology has given us a reliable solution. This technology not only cleans the water, but also removes the tiniest of impurities present in it. Let us know in this blog through 10 main points how it works and what is the scientific process behind it.
Basic understanding of reverse osmosis
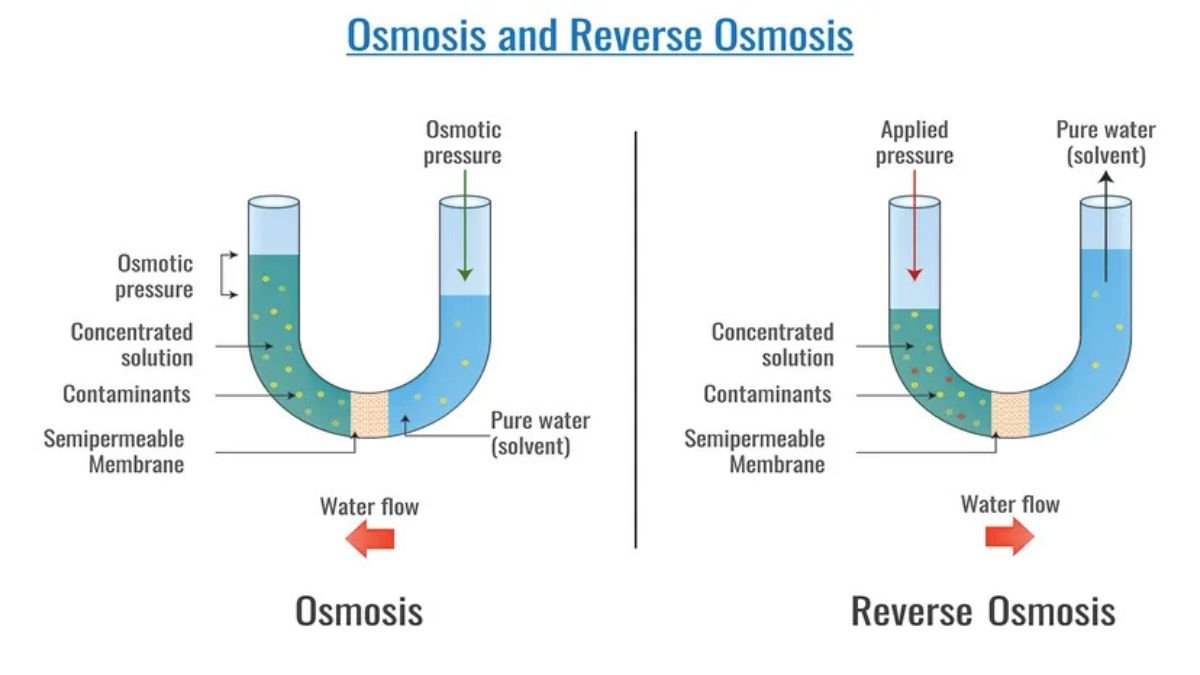
Reverse osmosis is a water purification technique in which water is passed through a semi-permeable membrane. This membrane has such small pores that they allow only water molecules to pass through, but stop salt, bacteria, viruses and other impurities. This process is exactly the opposite of natural osmosis, hence it is called Reverse Osmosis.
Structure and role of membrane
The most important part of RO is its membrane. It is made up of several layers, including a thin polyamide layer. The size of the pores in this layer is about 0.0001 microns. For comparison, the diameter of a hair is about 70 microns, that is, this membrane is so thin that it is impossible for bacteria and viruses to pass through it. This is why it makes water extremely pure.
Pressure force: the way to move water
In natural osmosis, water flows from the low concentration part to the high concentration part, but in RO we do it the opposite. For this, a high-pressure pump is used, which pushes the water towards the membrane. This pressure helps to separate salt, chemicals and heavy metals from the water.
Multi-stage filtration system
An RO system does not depend only on the membrane. In this, water is filtered in several stages:
- Sediment filter: To remove dust, soil and large particles
- Carbon filter: To remove chlorine and odor
- RO membrane: To block micro impurities
- Post-carbon filter: To improve taste and odor
After all these stages, the water becomes completely safe and tasty.
Cleaning of harmful elements from water
With RO technology, up to 95–99% of impurities can be removed from water, which include:
- Dissolved salts (TDS)
- Heavy metals like lead and arsenic
- Bacteria and viruses
- Nitrates and sulfates
This technology is especially beneficial for those areas where the TDS level in water is high.
Improvement in taste and odor
Often people think that the job of RO is only to make water safe, but it also improves its taste. When dissolved salts and chemicals are removed from the water, it tastes sweet and refreshing. Also, the chlorine-like smell also goes away.
Energy and maintenance requirement
Power is required to run the RO system, as it has a pump and several filters. Also, it is necessary to replace the membrane and filter from time to time, otherwise its capacity may decrease. However, with proper care, it works without any problem for many years.
Wasted water issue
One of the major controversial aspects of RO is that some part of the water is released as waste water (reject water). On an average, 2–3 liters of water can be wasted to make 1 liter of pure water. However, now many companies are making such RO systems in which this wastage is reduced and waste water can be reused.
Who needs RO the most
RO system is ideal for places where:
- TDS level in water is more than 500 ppm
- Heavy metals or chemicals are mixed
- There is high industrial pollution
- Water tastes salty or bitter
However, in areas where water is already clean and has low TDS, there is not much need for RO.
Future direction: Smart RO technology
Nowadays smart RO systems have also come in the market, which have features like TDS controller, mineral addition and IoT connectivity. This not only improves the quality of water, but you can also check its status from the mobile app. In the coming time, RO technology is moving towards becoming more energy-efficient and eco-friendly.
Conclusion
Reverse osmosis is not just a filtration technique, but a scientific art of making water drinkable. Its membrane science, high-pressure filtration and multi-stage process combine to make water not only safe but also improve taste and odour. Although it has issues like water wastage and maintenance, with the right technological developments it can become even better and more sustainable in the future.